Except for the linking verb list, the other categories break down into different types. The next list of verbs can be physical or mental. The list of helping verbs can be auxiliary or modal.
The list of irregular verbs shows verbs in different tenses. The purpose of auxiliary verbs is to help the action verbs. The latter are the verbs that describe what the subject of the sentence is doing.
For example, 'A person is crying/standing/eating. Here, crying, standing and eating are the actions. They accompany the action verbs and help in defining or changing the meaning of the sentence.
E.g. 'We were waiting for you at the mall.' On the other hand, linking verbs are those verbs that do not express any action. Here 'is' the verb that links the subject 'she' to the complement 'my friend'. Sometimes, it becomes difficult to distinguish between a linking verb and a helping verb.
For example, 'Julia was dancing with Bill at the party'. To determine that the 'to be' verb in this case is a helping verb, you need to see whether the 'to be' verb precedes the 'action verb'. In this case, the 'to be' verb is 'was' and the action verb is 'dancing'. That means, 'was' is an auxiliary verb that is helping the action verb 'dancing' to define time of the action. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause.
An example is the verb have in the sentence I have finished my lunch. Here, the auxiliary have helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, finished. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or auxiliaries.
Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Helping verbs, popularly known as auxiliary verbs, are words that occur in the sentence along with the main verb, to give a better idea of the tense of the sentence. Helping verbs enhance the quality and meaning of the sentence to a great extent.
The user can definitely tell about the actions if the proper helping verb is used to complement the main verb. In short, a helping verb can specify the link or relation between the verb and the time . The following helping verbs list and examples will shed some light on the usage of helping verbs in the context of rules of English grammar.
The verb 'have' can also be used as full verb or a helping verb. The way to differentiate between them is that if 'have' is used as an auxiliary verb, then it has to be followed by a main verb as well. The verb 'have' is used to make compound tenses in active and passive voices, and also used in the making of negative sentences and questions. It is an irregular verb that changes form according to tense. The opposite of a transitive verb is an intransitive verb. A verb is an intransitive verb if it is not used with a direct object.
Remember, only nouns, pronouns, and noun phrases can be direct objects. Prepositional phrases, adjectives, and adverbs cannot be used as direct objects. Once again, both action and stative verbs can be used as intransitive verbs. For more on that, see the section on modal auxiliary verbs or the one on copular verbs, both linked in the list of related guides at the end. A helping verb is a verb, such as "have," "can," or "will," that accompanies the main verb in a clause and helps to make distinctions in mood, voice, aspect, and tense.
It is a verb used in construction with certain forms of other verbs, as infinitives or participles. It thus accompanies and augments the meaning of a main verb; for example, "can" in "can do." Helping verbs are also called auxiliary verbs. The helping verb 'do' can also act as a full verb only in positive sentences. When do is used in a negative sentence, it is an auxiliary verb. The helping verb 'do' is also used to make questions for most verbs except other auxiliary verbs and the modal verbs.
"Do" is an irregular verb that changes its form according to the tense. The being/linking words in the sentences above are included in the being verbs list below. You can use words in the linking verbs list to connect the subject with other words in a sentence. Native English speakers can use helping verbs and modal auxiliary verbs without giving the grammar a second thought.
Of course, that's only true if we're talking about working in English. If you're learning a foreign language, you need to learn how its speakers express tense, voice, and mood. A good starting point for understanding how they do it is understanding how we do it.
Both modals and auxiliaries can be found on a list of helping verbs. Modals are usually followed by the infinitive of another verb. Just like the list of linking verbs, the list of modals within the list of helping verbs is also small and therefore easy to remember. You will notice that all of the linking verbs are on the Giant Verb List or the Giant Irregular Verb List PDF. Why? In contrast, none of the helping verbs are on the Giant Verb List or the Giant Irregular Verb List.
Once again, if the word is used as a helping verb, it is a helping verb (i.e., it is not a main verb, and it is not on the lists). However, if the word is used as a linking verb, it is a linking verb (i.e., it is a main verb, and it is on the lists). As I always say, it doesn't matter how the word looks; it matters how the word acts. Auxiliary verbs are also known as helping verbs and are used together with a main verb to show the verb's tense or to form a question or negative.
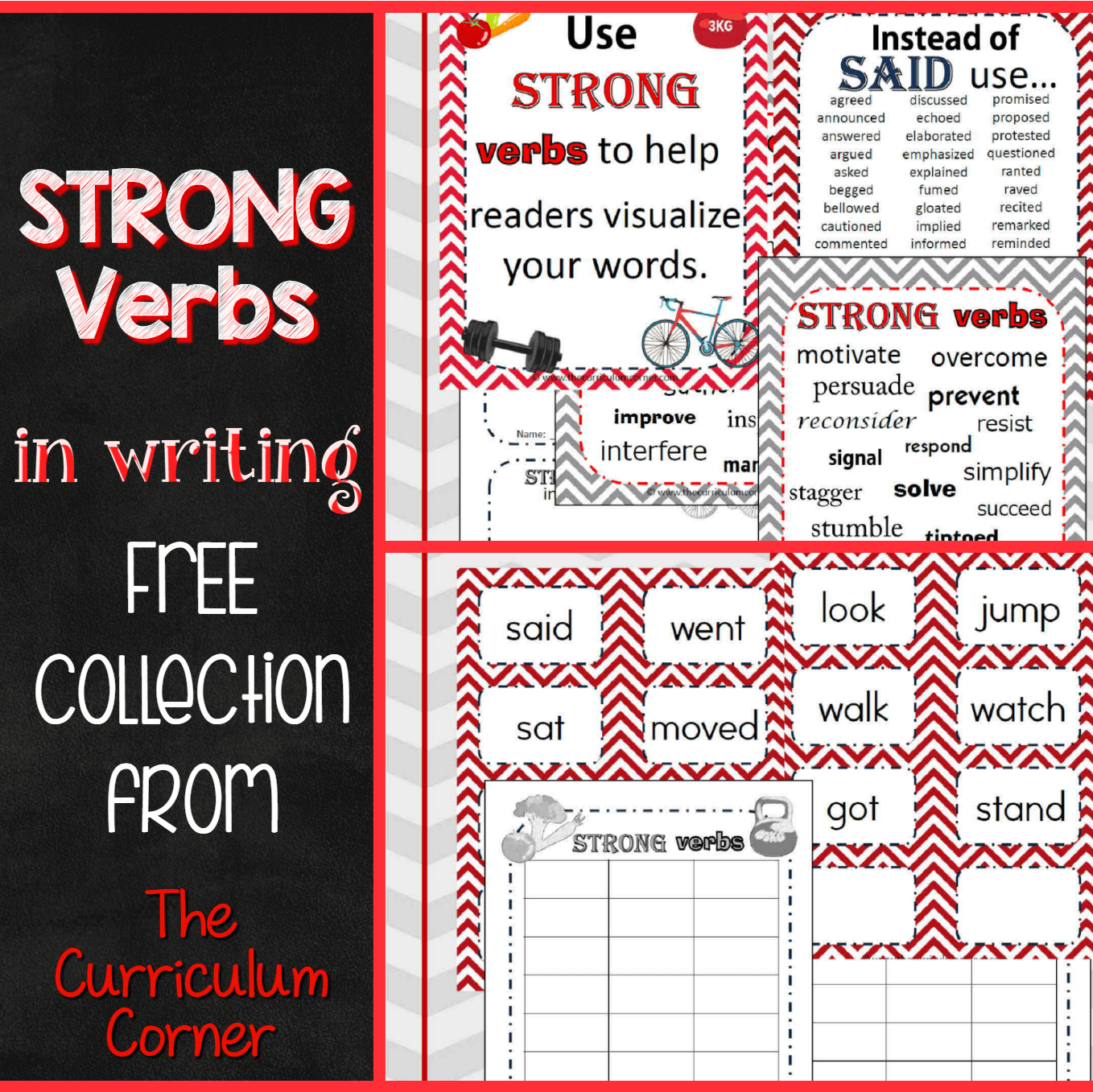
Common examples of auxiliary verbs include have, might, will. These auxiliary verbs give some context to the main verb, for example, letting the reader know when the action took place. To know more about linking verbs, we need to talk about action verbs. These verbs express some physical or mental action that a person, animal, object or even nature can do. Action verbs are words like drink dance, eat and swim.
Action verbs are different from linking verbs, which we can think of as "states of being" verbs. Helping verbs wo words hote hai jo sentence ke main verb ki help karte hai. Inhe English mein 'Auxiliary verbs' bhi kaha jata hai. Mainly 3 types ke helping verbs hote hai, jinke aage aur multiple forms hote hai. Helping verbs jane se pehle aiye 3 main helping verbs aur unke multiple forms jaan le.
Ab hum aise hi kuch helping verbs ki English to Hindi verbs list dekhenge. Regular and irregular verbs are categorized based on whether or not they end with a certain pattern in different tenses. These verbs are formed on the basis of how they look . A regular or an irregular verb, like any other action verb, is either a transitive verb or an intransitive verb.
Main verbs come in many shapes and sizes, just like their helpers. You can spot them if you can spot an action verb or a linking verb. Then, if you can answer the question "Who?" or "What?" after you spot the verb, you're even further down the pathway to grammatical expertise. Learn more about verbs and how they appear in a sentence with an irregular verbs list, complete with a helpful printable. For example, the sentence "Shannon is and plays in the field" doesn't make sense because is is a state of being and plays is an action verb.
Helping verbs are used before action or linking verbs to convey additional information. The main verb with an accompanying helping verb is called a verb phrase. Verbs are one of the eight main parts of speech, and we can't form sentences without them.
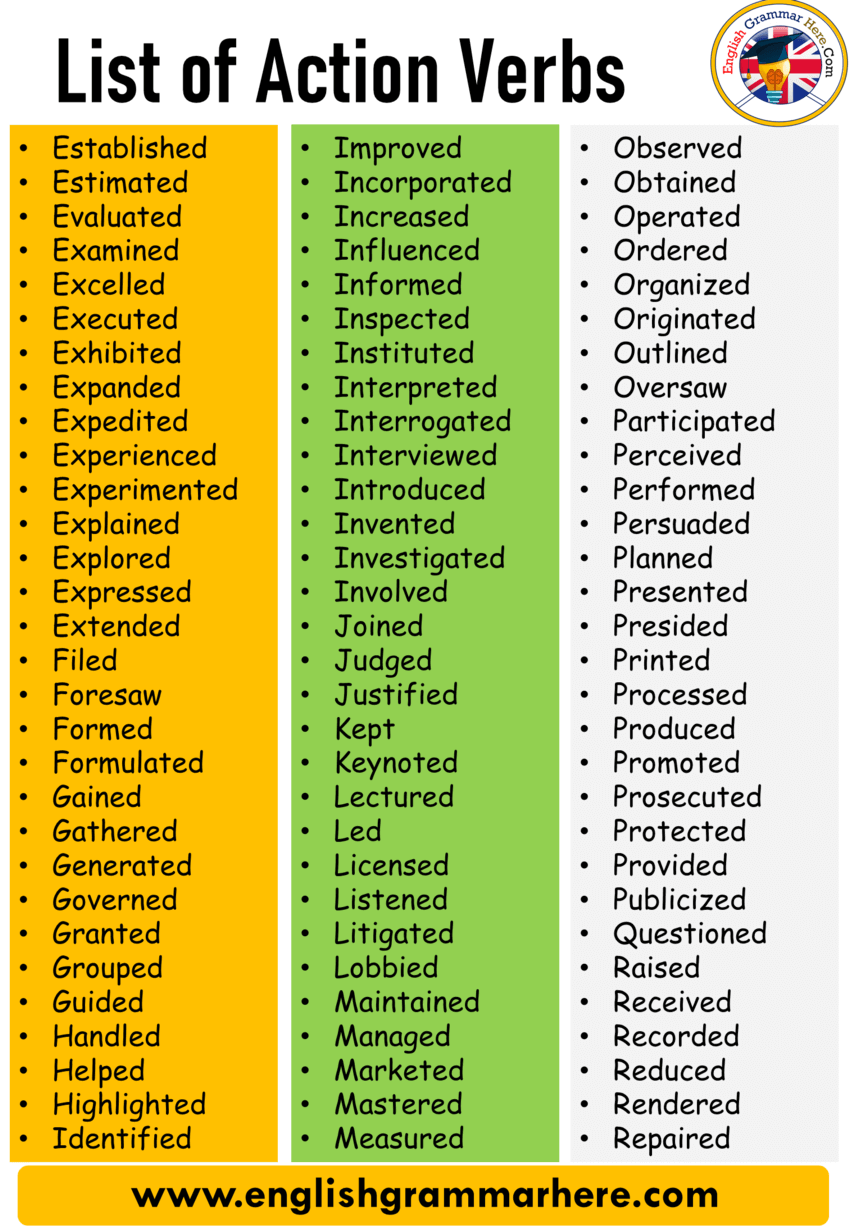
What Is Main Verb With Examples A verb explains the action of a sentence, but that's just one part of what verbs do. Use this guide to familiarize yourself with the types of verbs and what they do, and peruse this list of nearly 300 common verbs. There are over 1000 possible verbs you can use in the English language, and I'm sure you'll recall using some verbs on these lists more than others. This verbs list includes example sentences to help you expand your vocabulary and gain a better understanding of verb words and what they do. Most lists of linking verbs contain around 20 words. However, some lists contain a variety of common verb phrases (helping verb + verb).
There are three types of verbs; action, linking and helping. Most of the verbs you will use in conversation or writing will be action verbs or linking verbs. The different types of verbs have varying degrees of impact; it is important to choose the correct verb and type of verb to suit the particular situation such as business English. Helping verbs, also called auxiliary verbs, are helpful verbs that work with other verbs to change the meaning of a sentence. A helping verb combines with a main verb in order to accomplish different goals. These include changing the tense of the verb or altering the mood of a sentence.
Linking verbs do not describe an action, but tell about the state or condition of subjects. They link the subject with either a noun that renames it or an adjective that describes it. For example, the word "am" in the sentence "I am tall" describes the subject. There are some action verbs that function as linking verbs, such as grow. In the sentence "He grows tired," the verb describes the subject rather than an action, so it works as a linking verb.
The second of the three types of verbs is the helping verb. The main verb in a sentence may have one or more helping verbs. The main verb shows the action; the helping verbs do not show action, but they help to form the verb tense. The list is separated into action, helping, and linking verbs.
You may notice that some words like am, appear, was etc. can act as multiple types of verbs. When you see verbs that are on multiple lists, refer to the descriptions of the types of verbs above, and notice how the words differ in meaning in the examples. Do, have, and be change form to indicate tenses; modals do not. The appropriate forms of main verbs and helping verbs are discussed in this section. If the negative forms can't, don't, won't, etc. are viewed as separate verbs , then the number of auxiliaries increases.
The verbs do and have can also function as full verbs or as light verbs, which can be a source of confusion about their status. The modal verbs form a subclass of auxiliary verbs. Modal verbs are defective insofar as they cannot be inflected, nor do they appear as gerunds, infinitives, or participles. As a rule, my sons aren't thrilled to talk about grammar with me. Comments like "Wait—is this a linguistics thing?" and "Mom, Dad's talking grammar again!" have found their way into the conversation at times.
But one day I happened to be thinking, out loud, about auxiliary verbs. The "primary" auxiliary verbs—be, have, and do—are some of the most commonly occurring verbs in English. … Do is used to make main verbs negative or to form interrogative sentences, and it can also be used to add emphasis to a sentence. Transitive VerbsTransitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities that relate or affect someone or something else.
These other things are generally direct objects, nouns or pronouns that are affected by the verb, though some verbs can also take an indirect object, such as show, take, and make. In a sentence with a transitive verb, someone or something receives the action of the verb. Linking verbs are a special type of stative verb whose name gives a big clue as to what they do.
Linking verbs are used to link a subject with a subject complement. A subject complement describes or identifies the subject of the sentence or clause. Linking verbs can function as intransitive verbs, which do not take direct objects. The next verbs list you'll look at is the list of action verbs that are irregular, thus they are part of the irregular verbs list.
Well, verbs that do not follow the normal rules for conjugation fall into the irregular verbs list. These words could also be included on a list of action verbs describing physical motion. When you don't use these words in the literal sense, they become mental action words.

























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.